attackers can take benefit of encrypted tunnels
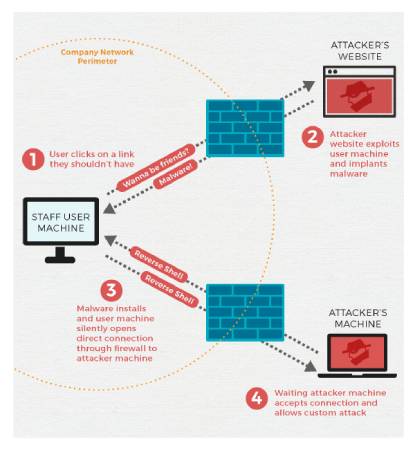
"As groups encrypt more visitors and using gadget
identities skyrockets, the opportunities for cybercriminals also boom,"
stated Nick Hunter, senior technical director at Venafi. "Any encrypted
tunnel can be exploited in a cyberattack, and leading organizations manipulate many
keys and certificates daily. This utilization will most straightforwardly
develop, and the drastic increase in keys and certificates will best make
securing encrypted tunnels extra tricky. Ultimately, businesses ought to
protect their encrypted tunnels or hazard being left at the mercy of cyberattackers.
Venafi security experts factor out that with outright
information of encrypted tunnels, cyber attackers can use them in opposition to
groups within the following five approaches:
Undetected movement in networks
Most large businesses use digital networks to hook up with multiple
workplaces and business partners. However, encrypted virtual community tunnels
are rarely inspected, allowing attackers to go undetected. Cybercriminals can
use those tunnels to transport websites.
Spy on private traffic to thieve facts
The maximum commonplace kinds of tunnels are in layered
security, consisting of a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer
Security (TLS). These tunnels offer a secure consultation between a browser and
a utility server. However, attackers can create guy-in-the-middle assaults on
secret agents on encrypted traffic and steal sufferer facts.
Terminal access
To defend Internet communications, groups create virtual
networks using Internet Protocol protection (IPsec). This often creates a
tunnel between a faraway and vital website, growing a perfect entry point for
cybercriminals. This sort of attack typically compromises established network
endpoints, and however, it may be the beginning of a more sophisticated attack.
Configuring phishing websites
Attackers regularly use stolen or compromised certificates
to set up a phishing website that the sufferer's browser trusts. Users can then
inadvertently percentage sensitive data with cyber attackers.
Because HTTPS sessions are relied on and infrequently
inspected, those assaults are often cross-neglected.
Privileged get entry to payloads
Tunnels created using Secure Shell (SSH) encryption are
rewarding goals for attackers. SSH keys deliver directors privileged access to
applications and structures, casting off the need to manually enter
credentials. Unfortunately, this also approaches that compromised SSH tunnels
can create a perfect environment for moving malicious payloads among document
and alertness servers.
"On a tremendous word, there are ways organizations can
cope with this threat," Hunter concluded. "Organizations need to
establish a database of trusted machine identities, regularly test for
untrusted identities, and take a proactive technique to defensive all system
identities. To do this, agencies need to centralize and review amassed
statistics and use automation to rotate keys and certificates regularly enough
to require converting a username and password. This can ensure that any safety
gear organizations rely on maintains a continuously updated list of relevant
keys and certificates to check out of their encrypted visitors. By protecting
the identities of these machines and integrating these facts into protection
tools, safety experts can ultimately begin to shed light on encrypted tunnels.


